Raised Floor
what is the raised access floor?
The raised access floor, also called “floating floor” or “false floor”, is a system created to meet the technological needs of technical rooms and allow easy accessibility and maintenance of infrastructure cabling system on Data Center and Good For Cooling Airflow .
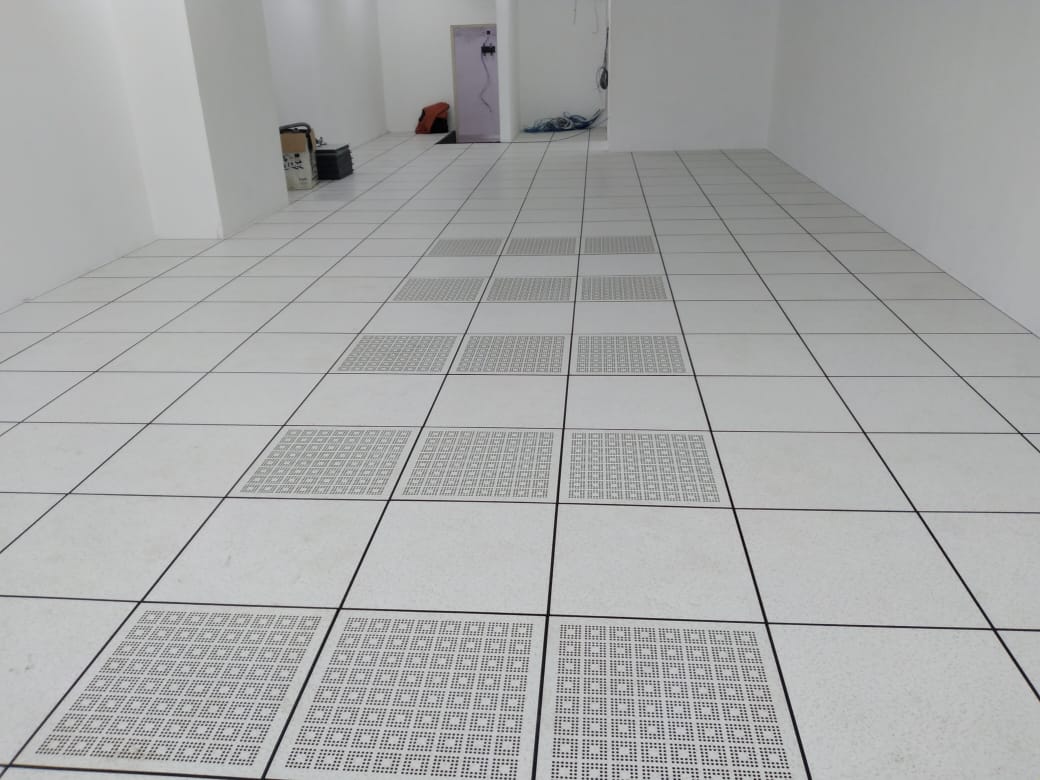

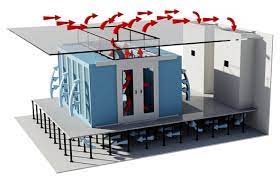
A raised floor in a data center is an elevated floor that is built two inches to four feet above a concrete floor. It creates a space that can be used for cooling, electrical, and mechanical services. In data centers, raised floors are also used as a way of distributing cold air. By using a raised floor, facilities not only reduce the amount of air needed to cool equipment, they also require less energy and improve temperature distribution across all of the cabinets. According to research on the impact of raised floors on thermal behavior in commercial buildings, the presence of a raised floor can potentially reduce the cooling load by as much as 40 percent. Combining this system with an AI cooling solution could deliver even greater savings.
Keeping Cool
Servers in data centers generate a huge amount of heat, presenting a major problem for data center designers and managers alike. When servers overheat, a common reaction is to consider getting extra cooling capacity, which is based on the assumption that the existing cooling infrastructure isn’t capable of maintaining a proper temperature. In reality, the problem may not be the result of insufficient capacity, but rather poor airflow management.
In order to keep the data center cool, a common practice is to install perforated raised floor tiles within cold aisles. These perforated tiles typically are not installed in hot aisles, unless there is a maintenance tile in place. These maintenance tiles give employees access in a warmer environment, so they can work in comfort. However, maintenance tiles should not remain in place permanently as they restrict air flow.
Sometimes grates are used as a quick fix for hot spots in a data center. However, since a grate can allow up to three times more air than the perforated raised floor tile, using them will exacerbate the issue. Managing the placement of raised floor tiles is critical. If not enough tiles are installed, the air can begin to recirculate. If too many tiles are installed, it can allow air bypass. If a choice must be made between recirculation and bypass, then bypass is preferable.
Cabling and Additional Equipment
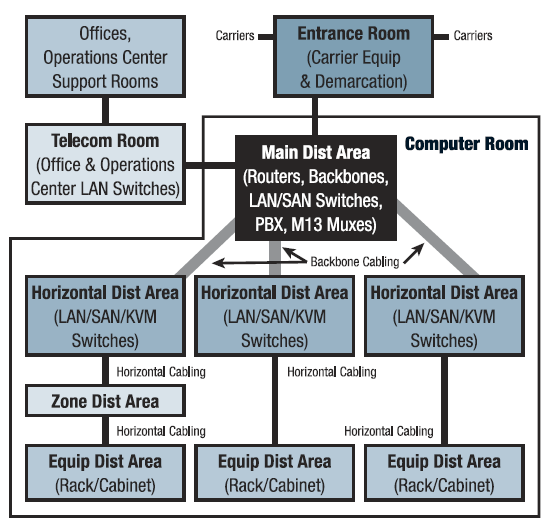
Having a raised floor in a data center also makes it easier to do equipment upgrades or install completely new equipment. This can include the installation of cabling and redeveloping the premises for other purposes. A raised floor is a good design strategy when there is a large amount of data center cabling to run. This is more efficient and can cost less than systems that are mounted near the ceiling. It can also help with the number of hidden cables and consolidation of physical ports and power plugs.
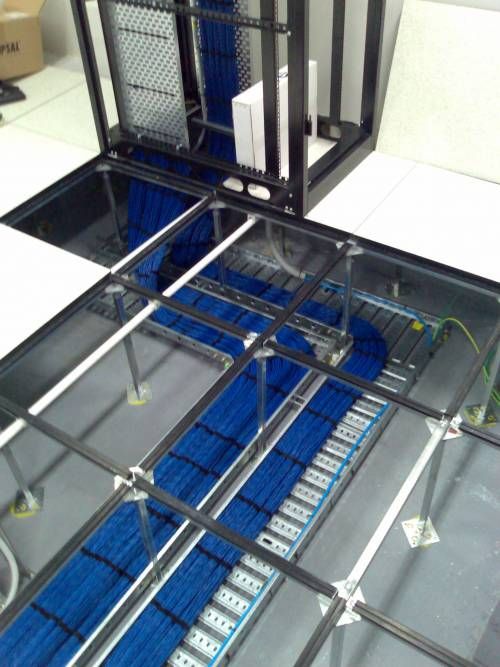

Running data center cabling under the raised floor tiles also helps to keep the data floor uncluttered and neat. Without overhead wiring systems in place, there’s nothing to block light fixtures and data center technicians don’t need a ladder to access cabling. Making a change to data center cabling is a simple matter of identifying the correct floor panel and removing it rather than accessing overhead trays that are located close to servers, light fixtures, and sprinkler systems.
Flexible Design
When setting up an initial design for a raised floor, data center engineers should consider the facility’s future development needs. This makes it easier to factor in the amount of free space needed to install both current and future equipment. The space beneath the raised floor tiles should be designed to allow cool air to circulate efficiently. Once a floor is installed, it’s critical for data center personnel to perform regular maintenance on the area, which includes taking special care to make sure it stays clean.
Since cold air can be channeled under the floor, a data center with a raised floor offers more versatility in terms of equipment deployment than a slab-based design. Rather than bolting the cabinets to the slab and directing cooling from above, raised floor tiles are more modular, allowing the facility to relocate equipment without the need to install new cooling infrastructure overheat.
Raised Floor Tile Maintenance
Cleaning underneath raised floor tiles helps keep out pollutants that could potentially pose a hazard to operations. Dust can get underneath the raised floor tiles and flow into equipment. The good news is that most data centers adhere to a regular policy of cleaning underneath the raised floors. This ensures the space created beneath the raised floor tiles is clean and free of contaminants, reducing the amount of dirty air getting pushed into the servers, which can increase the risk of equipment failure.
Cabling layout is very important in a facility with a raised floor. Just because the cabling will be out of sight doesn’t mean it can be out of mind as well. If too many cables are piled up in any area, they could significantly restrict or even block airflow, preventing some equipment from getting the cooling resources it needs. Data center managers need to carefully monitor how cables are arranged, especially when new lengths are being laid down or existing cabling needs to be replaced.
Raised floors may be one of the oldest design standards found in data centers, but they remain a popular strategy for managing cooling needs and cable deployment. By maximizing the potential of raised floors, data center managers can ensure that their facilities will remain efficient and effective for many years to come.
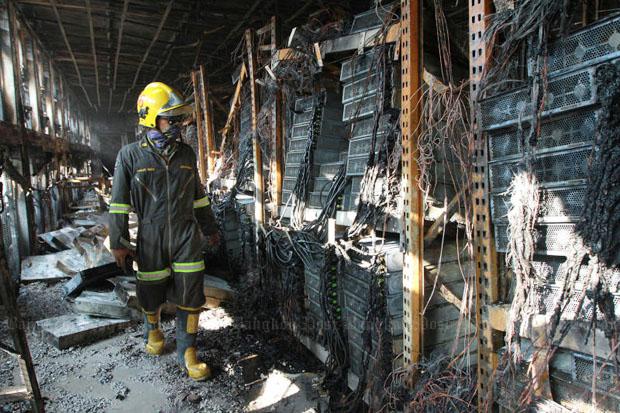




 Another Contributing is a Bad Connection , Over Loading and Dust .
Another Contributing is a Bad Connection , Over Loading and Dust .